2500+
Successful Projects

You might have heard of the capabilities of AI in software development, including integrating, assistance in coding, and so on, but think how powerful your software would be if it were entirely based on AI. They can offer great potential for progress and growth to businesses across multiple sectors.
Table of Contents
According to the latest report from Stanford University, 50% of businesses have successfully integrated AI capabilities into their operational frameworks. Furthermore, 76% of them looking to increase their spending on AI throughout the year 2025. If you are a business looking to invest in AI software development, this blog will help you understand the essential details involved in the process.
AI software development refers to building advanced systems or applications that use state-of-the-art AI and ML techniques to perform exceptional tasks that typically require human intelligence. These AI systems even do more than that by helping with better decision-making capabilities, pattern recognition, problem-solving, error handling, and process automation.
AI software systems allow businesses to automate complex operations and offer in-depth insights within a software program. Examples of such advanced systems include –
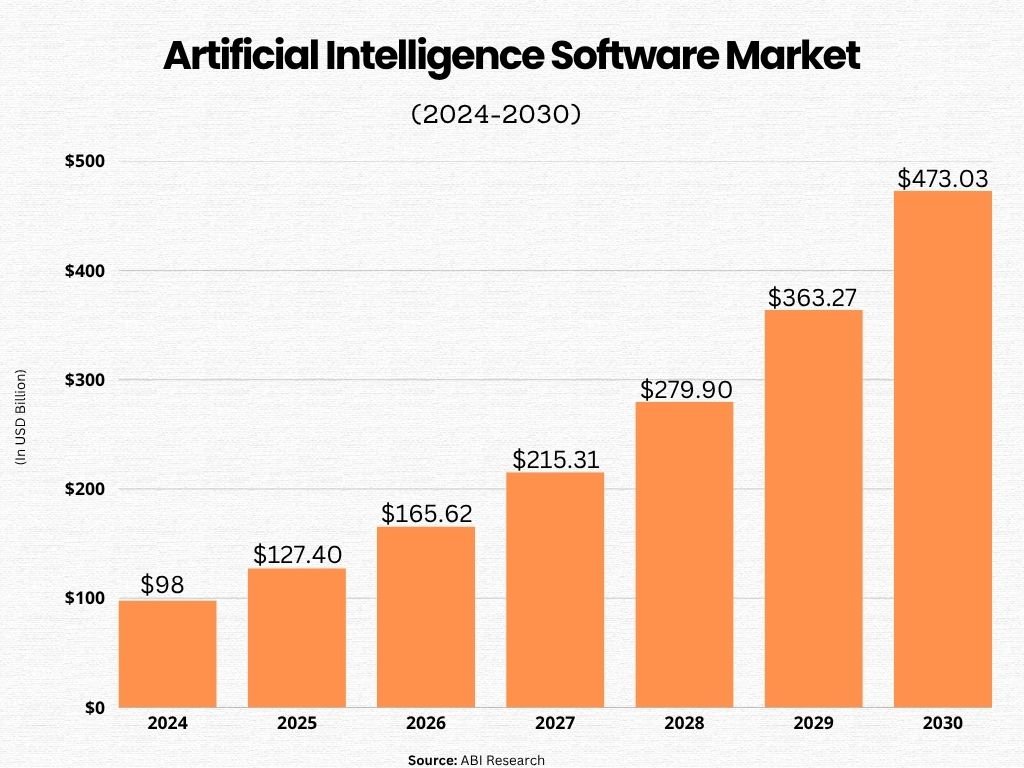
AI software systems are more than just a hyped trend, it has now evolved into mainstream technology. Its benefits for individuals and organizations are countless; here are the most prominent ones:
AI makes systems faster and more productive by cutting down on common human errors. Predictive analytics tools powered by AI eliminate even the smallest chance of human error. This saves time and resources while delivering precise and reliable results.
AI tools like chatbots and virtual assistants help businesses save money. They handle customer questions automatically, 24/7, reducing the need for large customer service teams. These AI systems provide quick, accurate answers, often faster and more efficiently than humans.
AI uses advanced algorithms to gather and analyze data from multiple sources quickly. It provides reliable insights and predictions, helping businesses make faster, smarter, and more unique decisions.
AI improves how businesses connect with customers by offering quick and effective solutions to their questions or concerns. AI chatbots, for example, can send personalized messages, making each customer feel valued and enhancing their overall experience.
AI’s predictive analytics tools spot patterns in your data, helping you make logical decisions in areas like business, finance, retail, and marketing. This lets you understand trends and make accurate predictions faster, giving you a clearer view of the future.
Creating strong AI software isn’t easy—it comes with its own set of challenges. But with careful planning, good data management, scalable systems, and a focus on ethics, these challenges can be tackled.
Adding AI tools to your existing IT setup can be tricky and might cause disruptions. To make this process smoother, pick AI systems that are flexible and modular. Also, test them thoroughly to ensure they work well with your current setup.
AI must follow ethical rules and data privacy laws. Stay informed about the latest regulations and best practices. Create clear rules for handling data and set up ways to ensure accountability.
AI needs lots of good-quality data to work well. Poor or biased data can lead to wrong results. Focus on collecting and preparing data carefully. Use techniques like data augmentation or synthetic data to fill gaps and reduce bias.
AI systems must handle more data and users as they grow. Build flexible system designs and use cloud services to manage this growth smoothly without slowing down.
Your choice of tools and technologies directly impacts the quality of your AI software. Without the proper resources, even the best ideas can fail. The tools you choose will determine your success.
Here’s a table listing the key technologies needed to create an AI system:
Components | Technologies |
Programming Languages | Python, R & Java |
Frameworks and Libraries | TensorFlow, PyTorch, Scikit-learn |
Data Sources | Data Sets & APIs |
Cloud Services | Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud |
Version Control Systems | GIT |
Data Visualization Tools | Tableau, Matplotlib |
Natural Language Processing (NLP) Libraries | NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit), spaCy |
Creating AI software requires both technical skills and smart planning to build solutions that are efficient, secure, and focused on goals.
To guide you, we have shared a five-step process that our software developers use to achieve the best results. Here’s what it looks like:
AI can tackle many challenges, but first, you need to know what problem you want to solve. This step is about clearly defining the issue your AI system will address.
Here’s a simple example to explain:
Suppose you run an online store and notice sales drop during holidays or weekends. To find out why, you analyze data and gather customer feedback. You discover that customers leave their carts because the checkout process is too long or product details are unclear.
Now, instead of saying “Sales are dropping,” your problem statement becomes: “High cart abandonment due to a slow checkout process and unclear product descriptions.” This is a problem AI can help fix. If you’re unsure how to define your problem, consider consulting an experienced software team for guidance.
Data is the backbone of AI systems. To build accurate models, you need plenty of high-quality data—typically at least 10 examples for each feature.
Start by collecting both structured data (like text, spreadsheets, or records) and unstructured data (like images or audio) from as many sources as possible. You can use existing datasets or gather new data through surveys, experiments, or web scraping.
Once you have the data, follow these steps:
Choosing the right algorithm depends on the type of AI software you’re building—whether it’s generative models, deep learning, or machine learning.
This is the most critical step in AI software development. Here, your chosen algorithm learns from the prepared data and becomes ready to make predictions or decisions.
Here’s a simple breakdown of the process:
Once your AI model is trained and tested, the next step is to make it work for users. A common way to do this is by creating an API (Application Programming Interface). This lets your software talk to the AI model hosted on a server and get predictions when needed.
For apps that need to work offline or in real-time (like mobile apps), you can embed the model directly into the software. This way, it can make predictions without needing an internet connection.
Make sure the AI features blend smoothly into the user interface. For example, if you’re adding a recommendation system to an online store, the suggestions should show up naturally on the right pages for users to see.
Many people think building AI software is extremely expensive, but that’s not always true. While it costs more than traditional technologies or off-the-shelf solutions, it’s still affordable for small and medium-sized businesses.
The final cost depends on your project’s needs and can vary widely. Here’s a rough breakdown of the costs and what influences them:
Total Estimated Cost Range: $130,000 - $500,000+
While the price tag may seem high, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
Developing AI systems is far different from any other software development; it requires you to take both legal and technical considerations in place. So, here are some important points to keep in mind while developing AI software:
AI systems learn from data, so their reliability depends on the quality of that data. However, the data used to train AI might contain hidden biases related to gender, race, or income levels. These biases can lead to unfair or discriminatory results, which can harm individuals and reinforce inequality.
To address this, developers must use diverse datasets and apply techniques to detect and reduce bias. Methods like re-sampling, re-weighting, and adversarial debiasing can help ensure AI systems make fair and unbiased decisions. This is crucial to prevent harm and promote equality in society.
AI systems are great at personalizing experiences for users by analyzing and interpreting data. But to do this, they need a lot of personal information. This raises big concerns about how user data is stored and used. If not handled carefully, there’s a risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, or misuse of sensitive information.
To tackle these privacy issues, AI developers must follow strict data protection rules, like the GDPR, and use strong encryption methods to keep user data safe. This helps ensure that personal information is protected and used responsibly.
The rise of AI has sparked many debates about its impact on jobs. Some worry that AI’s growing abilities will replace human workers in various industries, making manual labor less needed. In fact, many companies have already started laying off employees to save costs, as AI can often do similar or even better work at a lower price.
However, researchers suggest that AI can also improve the job market. For example, tools like the ATS resume scoring system help companies quickly filter job applications based on set criteria. Additionally, AI is creating new job opportunities in areas like AI development, data analysis, and AI ethics. Instead of just replacing jobs, AI can also transform and expand the workforce in new ways.
AI must be created and used in ways that are ethical and helpful for everyone. AI should reflect human values and principles like fairness, openness, and responsibility.
To make sure AI systems are safe and trustworthy, developers must carefully study how their creations might affect society. This includes understanding both the positive and negative impacts.
Developers should also work with a wide range of people, including experts, communities, and policymakers, to create clear rules and standards. These guidelines will help manage AI development and stop it from being used in harmful or unfair ways. By doing this, we can ensure AI benefits society while minimizing risks.
AI software development may seem tough at first, but it’s not if you follow the steps precisely outlined in this guide. With this detailed guide, the development process becomes easier. The first step in the process is identifying the needs and gathering the right data.
The next step is cleaning and preparing this data choosing the best AI model and head on for its training. Once satisfied with everything, deploy your advanced system for real-world use.
If you need professional assistance with your AI software development project, you need to contact the expert AI development company today.
To develop software using AI, start by defining the problem and gathering data. Choose appropriate AI algorithms (e.g., machine learning, NLP) and frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch. Train models with clean data, integrate them into the software and test them thoroughly.
AI is used in software development for automating repetitive tasks, code generation, bug detection, and testing. Tools like GitHub Copilot assist in writing code, while AI-powered testing frameworks improve accuracy. AI also enhances project management by predicting timelines and optimizing resource allocation, making the development process faster and more efficient.
AI is unlikely to replace coding entirely but will transform it. AI tools can automate routine coding tasks, assist developers, and generate code snippets. However, human creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making are still essential for complex software development. AI will act as a collaborator, enhancing productivity rather than replacing developers.
Popular AI tools for software development include GitHub Copilot for code assistance, TensorFlow and PyTorch for machine learning, and OpenAI’s GPT models for natural language tasks. Tools like Selenium and Testim automate testing, while Jira and Trello use AI for project management. Choose tools based on your project requirements and expertise.
Python is the most popular language for AI development due to its simplicity and extensive libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn. Other languages include R for statistical analysis, Java for large-scale systems, and Julia for high-performance computing. The choice depends on the specific AI application and developer preference.